You get only 2 seconds to convince your visitors about your relevance. If you fail, the visitor clicks the back button and leave your site for good. Here’s how you can stop it.
Search Engine Optimization has definitely come a long way since the heyday of the keyword marketing. The emergence of social media and mobile technology has completely changed the dynamics of search.
With the gradual shift in the way people search and the medium they use to conduct searches online, search engines including Google have fundamentally improved their search algorithms to offer better search results to their customers.
However, many SEO’s are still deploying the traditional SEO tactics that have lost their value considerably over the past couple of years or so. For the record, Google’s renewed algorithm considers over 200 unique signals including social popularity and relevancy in order to rank a web page in its search results.
In the post- Panda and Penguin era, the speculations about the effectiveness of SEO are rife, and almost every day we can find several SEO blogs ranting about the future of SEO. While keyword density and volume of links have lost their strength as potential signals for search ranking, many more properties are now being factored into ranking a page.
In this post, I’d like to talk about some critical factors that will fundamentally change the way we look at optimizing a website moving forward.
Sematic SEO
What is Semantic SEO? In order to understand what it means, I’d like to explain how Google conventionally ranks a webpage in its index.
In the good old days, the presence of keywords on web page was a decisive criterion to rank a webpage. Not only was it an unsophisticated method of ranking webpages, it was fundamentally so flawed that many SEOs gamed it to outrank potentially more relevant webpages in SERPs.
Today, search engines are gradually making a departure from the conventional methods of ranking webpages (read retrieving information) and we’re increasingly moving out of the phase that was dominated by keywords, anchor texts and links.
Semantic SEO, on the other hand, is not keyword driven. Rather, it’s designed to understand the intent of the user when they enter their search queries. When you use sematic search, Google will explore the relationship between the words of your query to better understand your intent and offer you more sophisticated results that address your query the way you intended.
The video below is an excellent guide to understand what semantic search is all about.
Mashable has recently published a great post on semantic search and how it can impact SEO in future. It’s a must read.
How will semantic search change the SEO?
According to the post, Google’s Knowledge Graph, which is the support system of semantic search, will offer more contextual information to the users rather than a list of webpages that are optimized with keywords. By doing this, Google effectively eliminates any chances of keywords being manipulated by black-hate SEO professionals. In fact, this will force the webmasters to frame content based on the user intent rather than keyword density.
As a result, content writers will have to figure out the actual meaning of keywords they are building content around, rather than just maintain an ideal keyword density. They will need to create better quality content that addresses all possible dimensions of a search query. This will essentially mean SEOs will spend far longer doing more research on creating content they are now.
Google Authorship
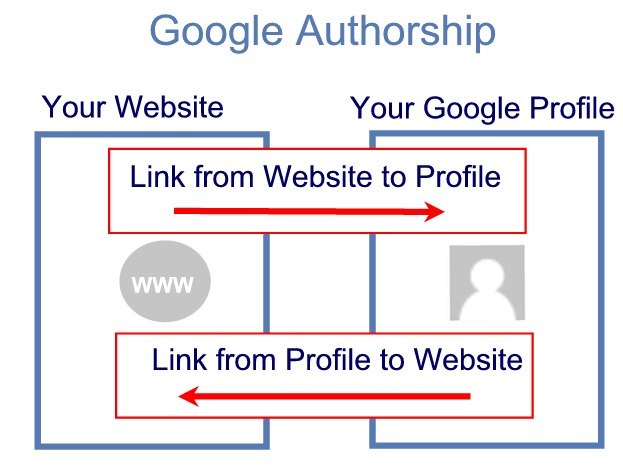 Back in the early days of Google, PageRank of an inbound link was a major contributing factor to the authority of a webpage. To put this in plain English, Google would rely on the topical authority and relevancy of a webpage based on the number and quality of other webpages it was linked from. But this gave rise to a whole industry of black-hate SEO practices including buying, selling and exchanging links across websites trusted by Google. In fact, those were the websites that were hit hard when Google released its Penguin Updates.
Back in the early days of Google, PageRank of an inbound link was a major contributing factor to the authority of a webpage. To put this in plain English, Google would rely on the topical authority and relevancy of a webpage based on the number and quality of other webpages it was linked from. But this gave rise to a whole industry of black-hate SEO practices including buying, selling and exchanging links across websites trusted by Google. In fact, those were the websites that were hit hard when Google released its Penguin Updates.
But things have changed since then. Today, Google is advocating the use of rich snippets and structured mark-up data on websites to make them user friendly. Google Authorship is one of those guidelines and is a step forward into the world where content of a website will be judged purely on the basis of topical authority. Therefore, having registered with Google Authorship, you will able to drive influence as a thought leader in your niche.
In fact, when Google officially introduces AuthoRank/AgentRank in future, it will drastically influence the topical authority of webpages authored by authoritative thought leaders in the industry. It will effectively mean that pages with high AuthorRank will establish higher relevance as compared other webpages. Some SEO experts call it Search Entity Optimization. Here’s a great post to talk about how search is moving from pages to entities.
Co-citation and Co-occurrence (Social Citation Strength)
 If I told you that your website/blog could rank higher for competitive keywords without even getting any backlinks from other sources, it would probably a bit difficult for you to believe, right?
If I told you that your website/blog could rank higher for competitive keywords without even getting any backlinks from other sources, it would probably a bit difficult for you to believe, right?
Well, brace yourself! If SEO analysts are right in their observations, Google has already started ranking webpages in the top three spots of its SERPs that are not even optimized for the target search queries anywhere in their title tag or page content.
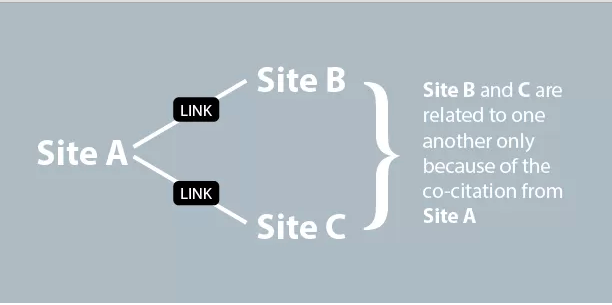
Co-citation and co-occurrence are some of the revolutionary directions Google is in the process of taking to kill the anchor-text manipulations and improve search results.
In this amazing post on Search Engine Journal, the author has defined Co-citation as the process of link building without actual links. He says co-citation, unlike anchor-text, doesn’t have to involve a link back to the page. In fact, it is the logical relationship (similarities) between two webpages based on the third-party webpage that successfully mentions the first two pages in correlation with each other. Google identifies such a relationship between the pages and uses it an important search engine ranking factor.
SEO experts believe the official introduction of co-citation and co-occurrence may kill the importance of anchor-text in the future. Some believe Google has already started implementing it as a ranking factor. Watch Rand Fishkin’s Whiteboard Friday to get a proof of this revelation.
How to Increase Social Citation Strength?
Experts believe improving the quality of your webpage information can improve your chances being cited on other sites and social networks which will dramatically improve your social citation strength.
SEOs will need to create content that is worthy of being mentioned on social networks such as Facebook, Quora and Twitter in a way that Google notices it. Moreover, it will depend on how well you market your brand and actively participate on forums and social media sites.
If you’re an SEO professional, there’s never a better time to shake up your old SEO myths like now and get ready to drive your campaigns purely based on the quality of information moving forward.
If you find this post useful, be sure to share it with your friends. Thanks!












